
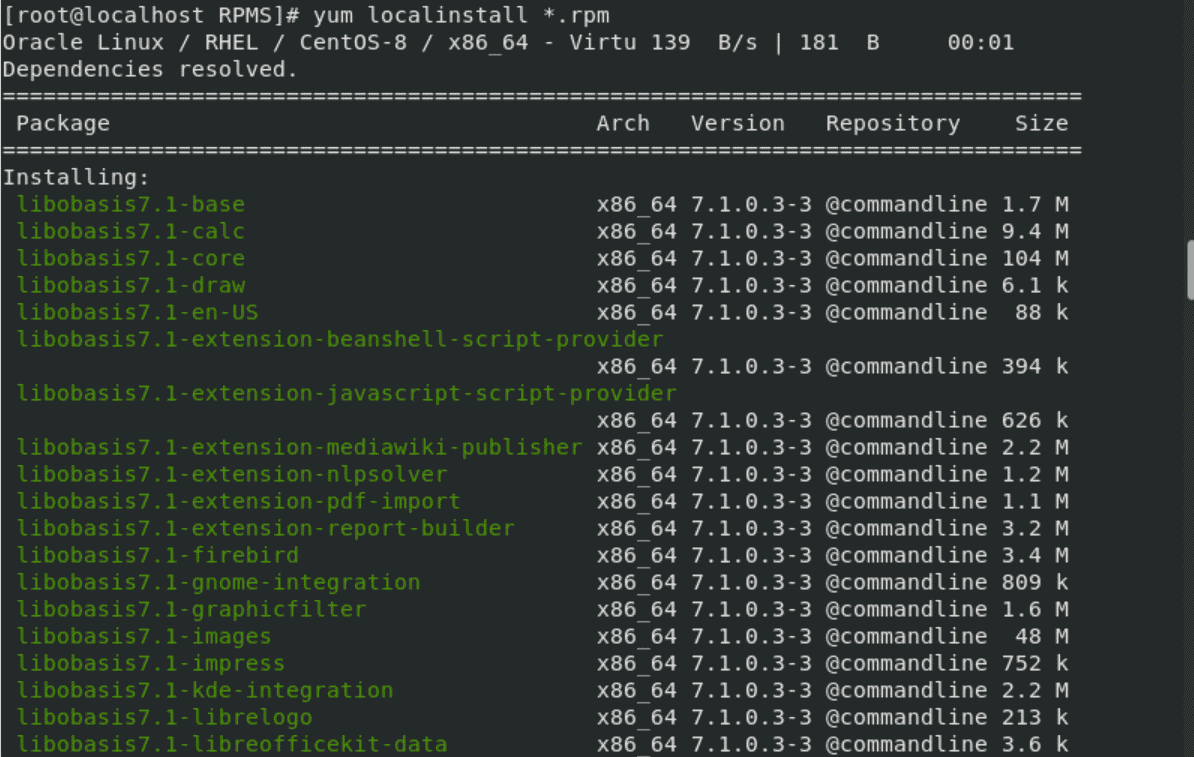

We can manage the rpm commands using appropriate actions with root privileges. Note: In Linux, please remember we must be a super user at the time of installing the RPM packages. The following is the rpm site's list where we can search and download the RPM packages.

Verify: This mode is used for verifying the RPM packages.Upgrade: It is used for updating the available RPM packages. This manual explains how to boot the CentOS 7 installation program (Anaconda) and how to install CentOS 7 on AMD64 and Intel 64 systems, 64-bit ARM systems, and 64-bit IBM Power Systems servers.It also covers advanced installation methods such as Kickstart installations, PXE installations, and installations over VNC.Remove: It is used for erasing, removing, or uninstalling the RPM packages.Install: This mode is used for installing the RPM packages.It includes the actual details of the packages like what it is, version info, dependencies info, from where it comes, etc. RPM keeps the details of every installed package in a database, i.e., /var/lib/rpm.If we have installed any package with source code, the RPM would not manage it. RPM is a single way for installing packages upon Linux systems.RPM (Red Hat Package Manager) is free and published upon GPL (General Public License).It only implements with those packages that were created in. It contains compiled software libraries and programs required by the packages. The tool permits system users and administrators for installing, updating, uninstalling, querying, verifying, and managing system software packages in Linux/UNIX operating systems.įormerly, the RPM is called the. It is an open-source package manager (default) and the most famous utility of package management for Red Hat-based systems such as Fedora, CentOS, and RHEL.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
